Penn Cloud
Published:
This is a course project for CIS505 Software Systems(Spring 2024) at University of Pennsylvania.
Our team built a Distributed Penn Cloud Application, supporting User Service, Email Service, Drive Service, and Monitor Service.
Here is the Porject Report and Github Repo.
The diagram is as follows:
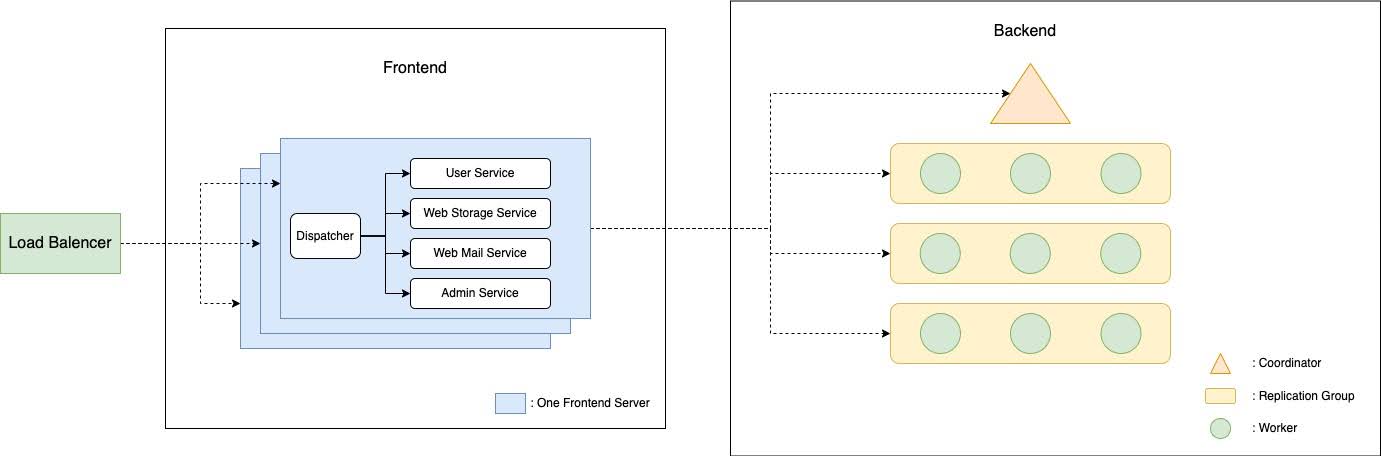
Components
Key-Value Store
Our PennCloud application includes a robust key-value store inspired by Google’s BigTable, featuring persistence, replication, and fault-tolerance.
- Master-slave archiecture: One coordinator and several replication groups.
- Sharding: Utilized the Hash slot for data sharding, distributing rows among replication groups. Each replication group contains one primary node and two secondary nodes.
- Sequential model: Maintained strong consistency with the help of sequentialized requests, centralized checkpoint, Append-Only File(AOF) logging, 2PC-like protocol and row-level locking.
- Fault-tolerance: The system provides fault tolerance by supporting all operations and maintaining consistency at least one node (any one node) in one replication group is active. In our case, each replication group has a size of 3. The system handles the node crashing at any time, including during any operations or during replication forwarding. This is achieved by enabling worker nodes to report other inactive worker nodes to the coordinator during their communications.
- Recovery: Each worker node supports both local recovery, by reading the checkpoint file and AOF log files, and optimized remote recovery, by trying to transfer the log file difference before transferring the whole checkpoint file.
Frontend Server
The frontend of our PennCloud application is built using an MVC design, inspired by Spring framework, ensuring scalability and ease of maintaince.
- Workflow: The web server handles HTTP requests, parses them, and dispatches them to appropriate handlers based on the request path and method.
- Filter: The Spring-like filter chain is implemented for Authentication management.
- Authentication: Utilized JWT in Cookies, providing user isolation and management.
- Various User Interactions: Implemented Dynamic Content loading and RESTful API design.
- HTML/JavaScript: Utilized the Twilwind CSS for storage service and emial service.
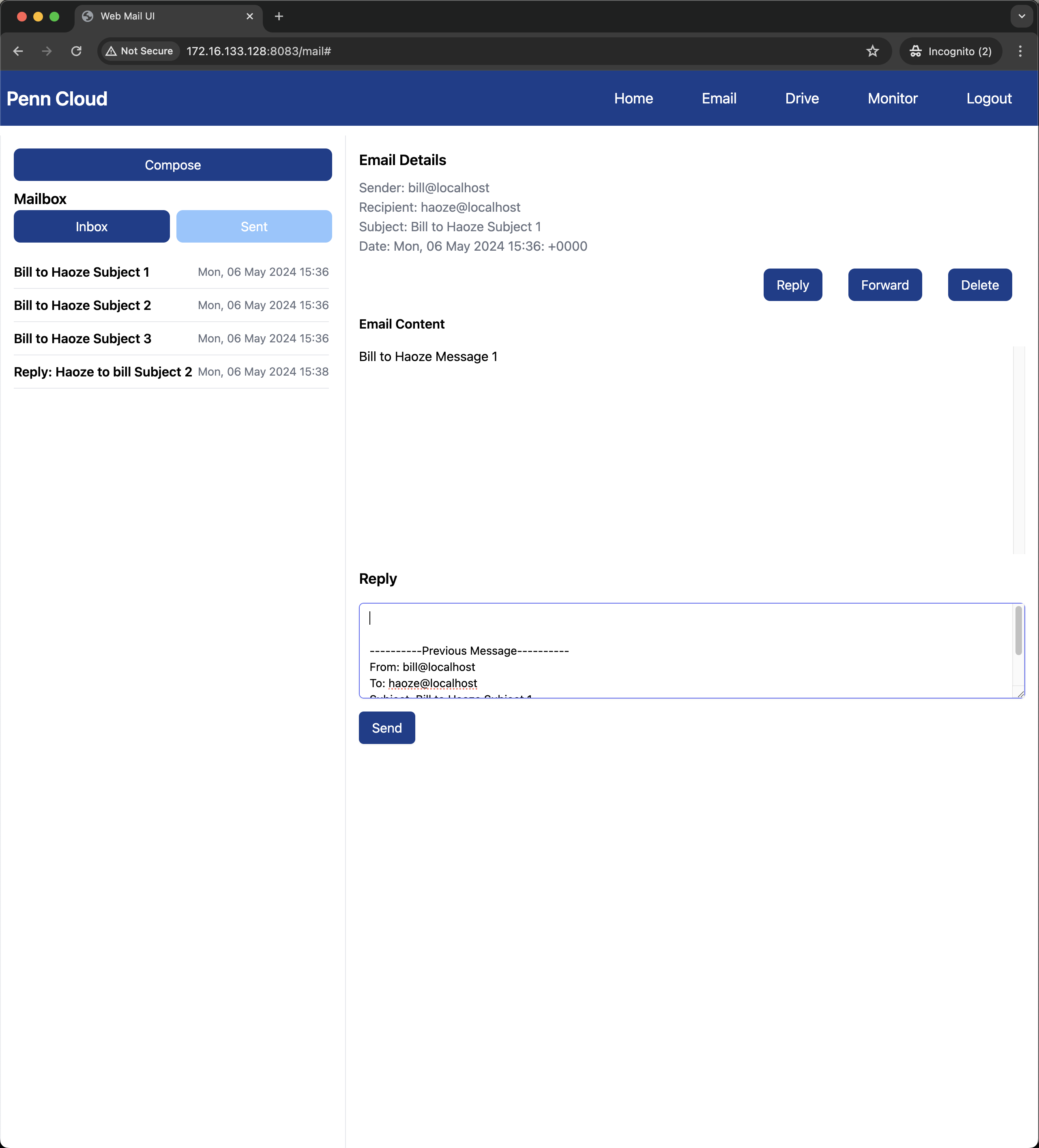
Webmail Service
The webmail service is designed to handle both internal and external emial communications.
- SMTP Server/Client: Implemented an SMTP server to accept emails from within and outside the sytem and an SMTP client to send emails to local and remote user, with the VPN for DNS support.
- Service Functionality: The service contains web-based interface for managing mails, like viewing, composing, and deleting messages.
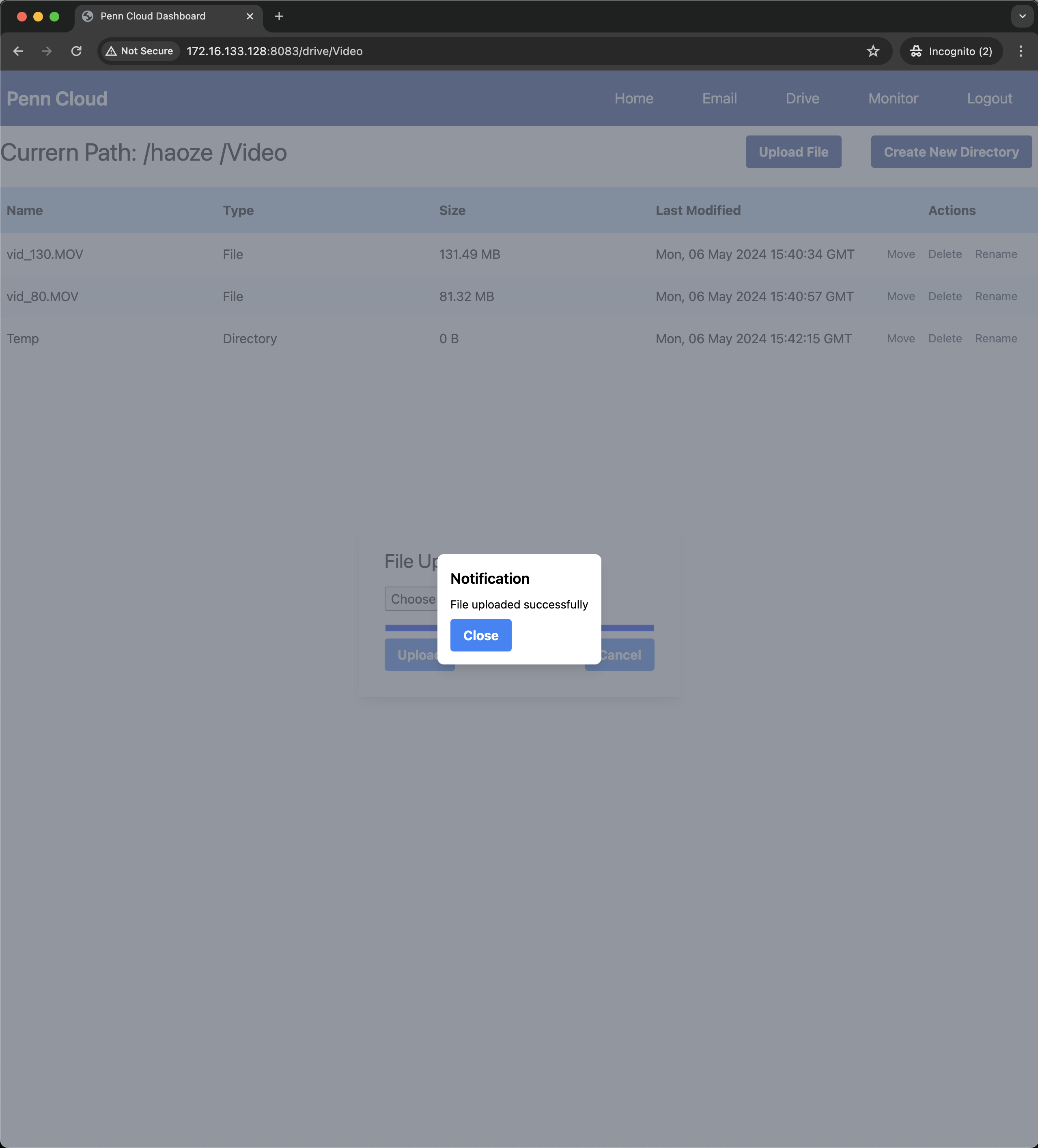
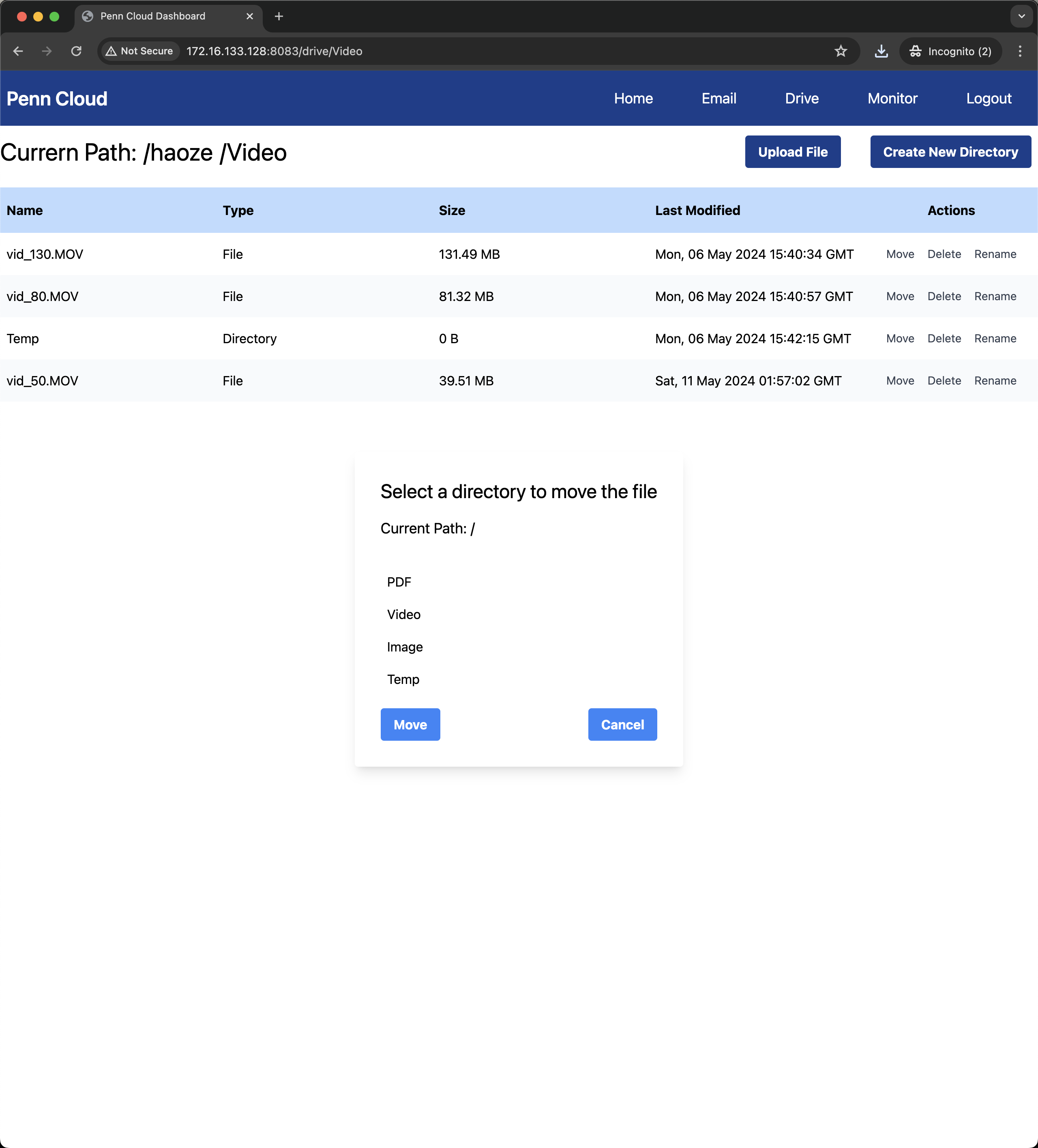
Web Storage Service
The web storage service mimics the functionality of Google Drive, allowing users to upload, download, and manage files and directories.
- Service Functionality: The service supports various functionalities, such as creating, moving, renaming, and deleting directories and files.
- Large File Management: Large files are chunked into for storage, improving the fault-tolerance and load balancing.
- Binary File Encode/Decode: As for binary files, they will be encoded by BASE64 algorithm.
- Design Architecture: A tree-like folder structure decouples the file structure from the actual data, enhancing the performance and scalability.
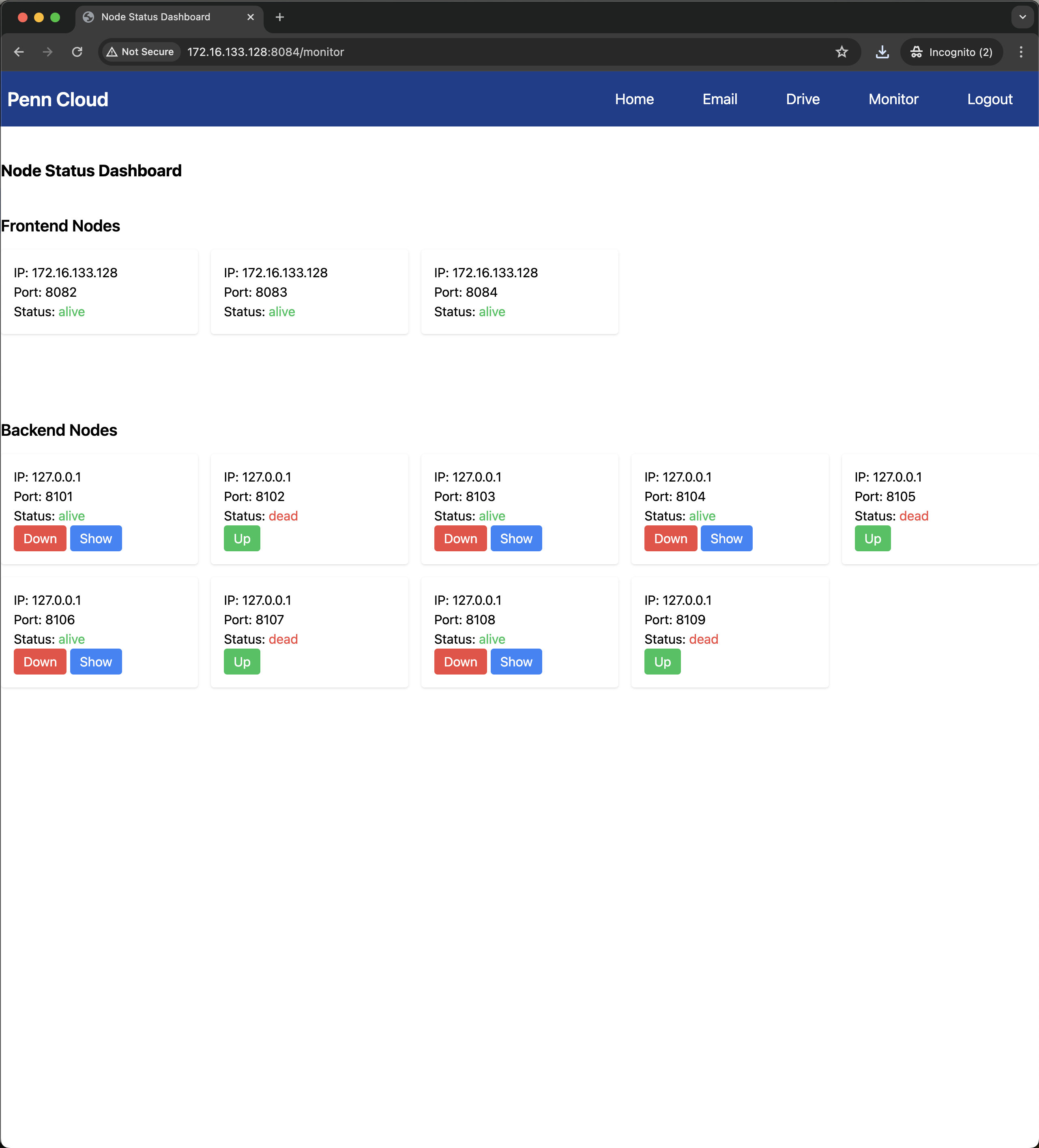
Admin Console
The admin console is for monitoring and managing the PennCloud system. It provides real-time status updates of frontend and backend nodes, displaying whether they are alive or dead.
- Service Functionality: The console allows administrators to start and stop backend nodes, view the key-value data inside the alive nodes, and manage the overall system health.
- Monitor Design Archiecture and Strategy: The monitor is a two-layer architecture, the coordinators of frontend/backend utilize the Push-based strategy to gather information from worker nodes, and the monitor uses the Push-based strategy to gather information from both coordinators.
Load Balancer
The load balancer in PennCloud ensures efficient distribution of user requests to frontend nodes. Upon startup, frontend nodes register with the load balancer using the configure file.
- Redirect Policy: The load balancer redirect the incomming requests to available nodes based on round-robin and heal-based check.
- Coordinator Duty: The load balancer also communicates with the admin console to report the status of the frontend nodes.
Some screenshots of our application:
 |  |
 |  |