Cloud-based Distributed Search Engine
Published:
This is a course project for CIS555 Internet & Web System(Spring 2023) at University of Pennsylvania.
Our team built a Cloud-based Distributed Search Engine, with four components using self-crafted framework, deployed on AWS EC2. The diagram is as follows:
Here is the Porject Report and Github Repo.
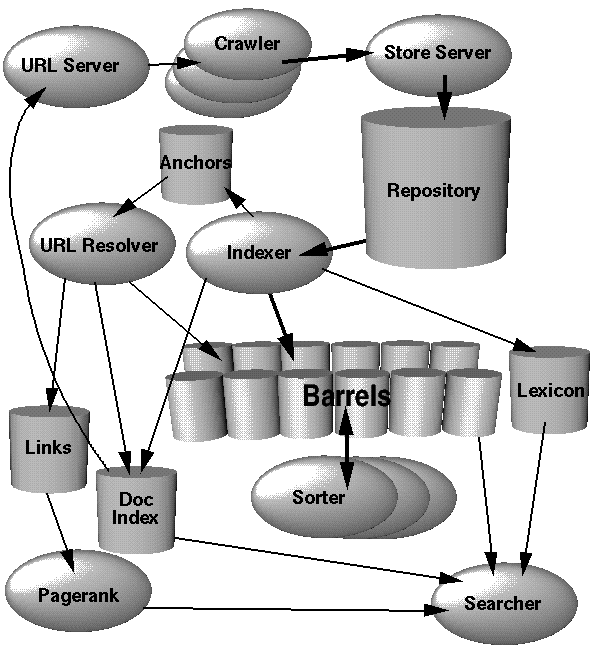
Framework
- HTTP server framework: Our HTTP server framework supports persistent connections, concurrent requests handling through thread pool, and robust error handling. It also supports dynamic content and routing inspired by Spark framework, allowing the server to manage GET, PUT, HEAD, and POST requests dynamically. In addition, the framework includes session management and CA-signed TLS certificate for secure communications.
- Key-Value Storage: Our Key-value storage system is an in-memory distributed key-value store with extended persistence, inspired by Redis. Utilized a master-slave architecture and consistent hashing for data sharding, the system ensures efficient data distribution. Persistence is achieved through Append-Only File(AOF) mechanism, complemented by a background garbage collector that periodically clean the file. After the crash and restart, the recovery mechanism rebuilds in-memory indices. The data schema is table-based, including table name, row key and column key. In addition, a user-friendly interface to easily monitor and manage the tables in system.
- Data analytics Engine: Our Distributed Analytics Engine, Flame, inspired by Apache Spark, supports core and advanced functionality including parallelizing data across nodes, applying operation like
flatMap,fold,joinand so on. It integrates seamlessly with a key-value store for efficient data management, distributing workloads evenly among multiple workers. Flame supports a comprehensive set of data transformations and aggregations, making it a powerful tool for large-scale data analytics.
Components
Crawler
The crawler is designed for efficiency and scalability, using a distributed architecture with eight workers and a master server. The crawler manages a frontier of URLs, ensuring that newly discovered URLs are prioritized and processed. URLs are encoded to distribute evenly among workers, and the queue’s persistence ensures resilience against worker crashes. Each worker adheres robots.txt rules, and the master monitors the system to ensure robustness and minimize downtime.
Indexer
The indexer processes the crawled data to create index table. We implemented a unigram tokenizer with stop words dictionary to filter out common, insignificant words, thus optimizing storage and search efficiency. Stemming is to compress different forms of a word to its base form. The indexing process involves parsing the crawled web content, tokenizing words, removing stop words, applying stemming, building inverted index table, and computing the Term Frequency(TF)/Inverted Document Frequency(IDF) table. The generated table will be used in the ranker to get the relevant score for accurate search.
PageRanker
The PageRanker componet calculates the importance of each page based on the link structure of the web basd on Iterative PageRank Algorithm. We addressed the challenge of handling large datasets by partitioning the crawled data into manageable chunks. Each worker calculates PageRank across for its assigned chunk, and these scores are aggregated to produce the final ranking. Since the bottleneck is at the disk I/O, we apply some mechanism like caching the intermediate result and compute based on it rather than disk data, which significantly improve the performance. Dispite the optimization, the process remains disk I/O intensive, which is the bottleneck of our KVS.
Frontend
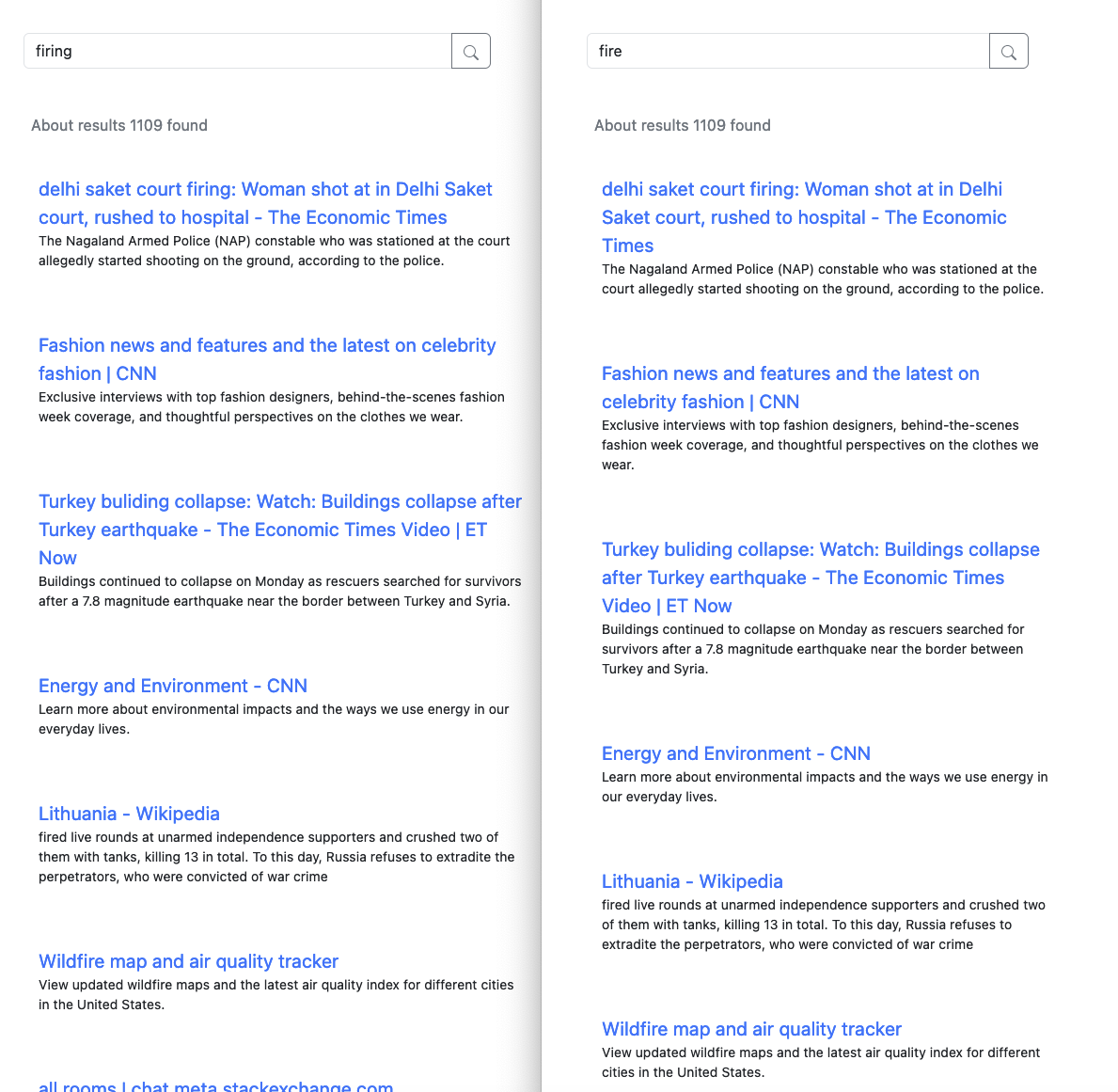
The frontend of our search engine is designed to be user-friendly and efficient, featuring a clean and responsive interface. It supports advanced features like spellcheck, using the Bing Spell Check API to suggest the correction for misspelled queries, and infinite scroll to dynamically loads more reshe user scrolls down the page. The frontend communicats with the backend to retrieve search results, which are ranked based on TF/IDF and PageRank scores. This combination ensure that the most relevant and authoritaive pages are presented to the user.
Some screenshots of our search engine: